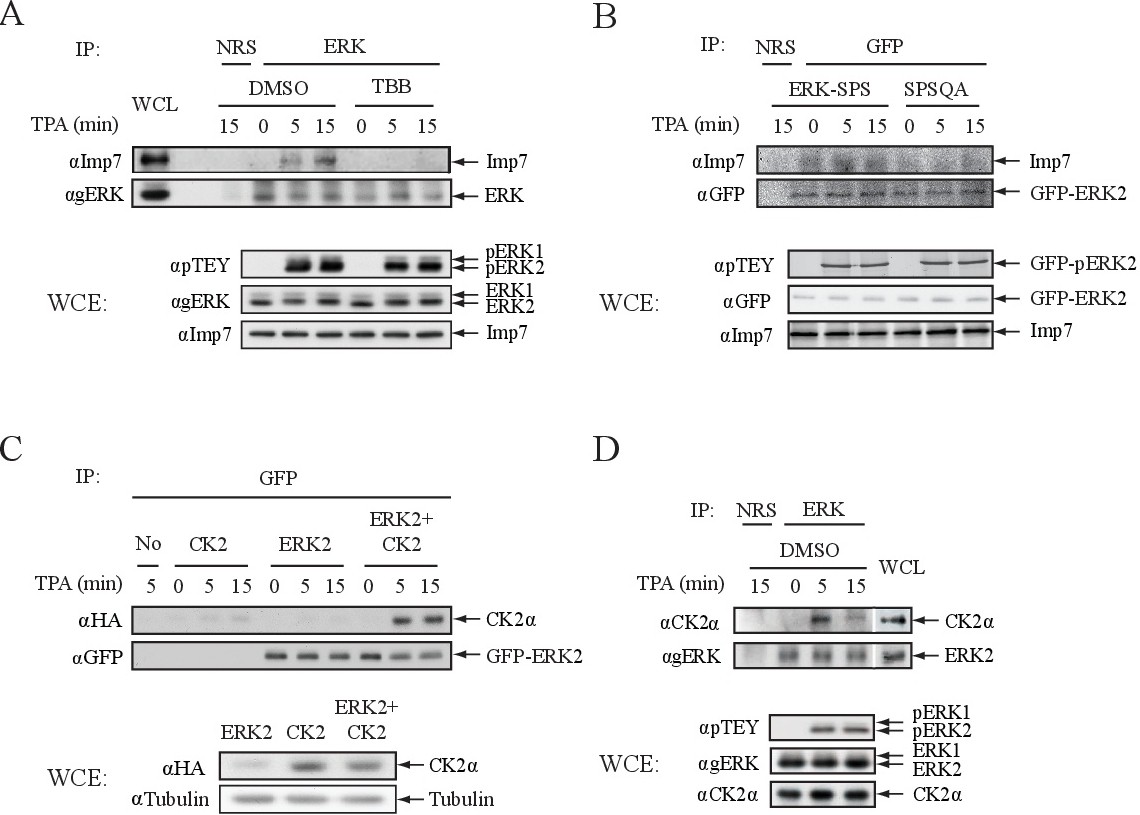
Fig. 4. ERK binding to Imp7 and CK2. (A) Imp7 interaction with ERK dependents on CK2 phosphorylation of ERK's NTS. HeLa cells were serum-starved and treated with TPA (250 nM) for the indicated times. ERK was immunoprecipitated using agERK Abs or normal rabbit serum (NRS) that served as an irrelevant Ab control. Co-immunoprecipitated Imp7 was detected by Western blot analysis using aImp7 Abs (upper panel). ERK activation and Imp7 amount were determined using the indicated Abs. (B) Mutation of E248 and D249 prevents the interaction of ERK with Imp7. HEK-293T cells were transfected with the GFP tagged plasmids of ERK2-WT (SPS) and ERK2-SPSQAA, serum starved and stimulated with TPA (250 nM) for the indicated times. ERK constructs were immunoprecipitated using either aGFP Ab or NRS control, and co-immunoprecipitated Imp7 was detected by Western blot analysis with aImp Abs. ERK activation and Imp7 amount were detected using the indicated Abs. (C) Ectopically expressed CK2 interacts with overexpressed ERK2 in a stimulus-dependent manner. HEK-293T cells were transfected with HA-tagged CK2a, GFP-ERK2 or both plasmids. Thirty-six h after transfection, the cells were serum-starved and then stimulated with TPA (250 nM) for the indicated times. ERK2 was immunoprecipitated using aGFP Ab, and the co-immunopreciopitated CK2a was detected by Western blot analysis using aHA Ab. The amount of expressed proteins was detected with aHA and aTubulin Abs. (D) Stimulus-dependent interaction of endogenous CK2 and ERK. HeLa cells were serum-starved and then stimulated with TPA (250 nM) for the indicated times. Endogenous ERKs were immunoprecipitated using either agERK Ab or NRS control, and co-immunoprecipitated CK2a was detected by Western blot analysis with aCK2a Ab. ERK activation and CK2 loading were detected using the indicated Abs.